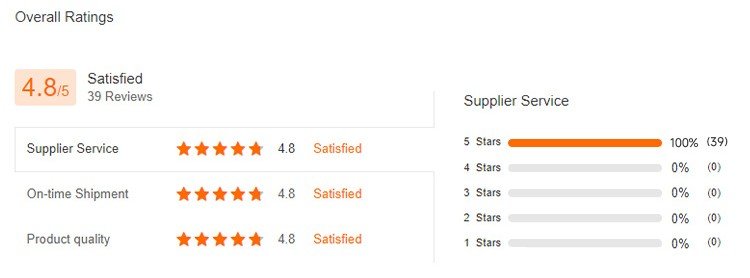
Kale generally has the effects of assisting in enhancing immunity, supplementing nutrients, and promoting digestion. Its taboos are generally people with allergies. 1. Assisting in enhancing immunity: Kale is rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, which can improve the body’s immune system function and help fight free radical damage, thereby helping to prevent the occurrence of diseases. 2. Supplementing nutrients: Kale is rich in a variety of nutrients, including vitamin A, K, B6, folic acid, iron, calcium and potassium.
The effects of kale are as follows:
1. Prevent and treat constipation: Kale is rich in fiber and water, both of which help prevent constipation and promote the normal functioning of the intestines and a healthy digestive tract.
2. Supplementing nutrition: Kale is rich in vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin B and other nutrients, which has a significant effect on supplementing human nutrition.
3. Weight loss: Kale contains iron, which increases the oxygen content in the blood, inhibits the production of fat, and has a good effect on weight loss.
4. Delaying aging: Kale contains beta-carotene, which can increase the activity of red blood cells. Peroxide free radicals can accelerate human aging, while β-carotene can neutralize peroxide free radicals in the body, thus playing a role in delaying aging.
Taboos of kale are as follows:
1. Because kale is rich in dietary fiber, people with gastritis, gastric ulcers, and gastric bleeding should strictly control their consumption to avoid the aggravation of ulcers and bleeding due to the stimulation of dietary fiber.
2. Kale is a cold food. People with weak constitution, spleen and stomach deficiency, and diarrhea should not eat too much. People with low blood pressure, and those who are prone to numbness or cramps in their hands and feet should not eat too much.